Introduction
Under the J-Credit Scheme, Japanese enterprises, local governments, agricultural workers, or forest owners can reduce carbon emissions by introducing energy-saving equipment, using renewable energy, improving industrial processes and agricultural management, as well as waste management and forest carbon sinks. Entities can obtain the certificate of carbon reduction or absorption (J-Credit) after being recognized by the competent authority. In response to carbon reduction requirement, large enterprises can purchase J-Credit certificates from the aforementioned to replenish carbon reduction quotas when they have difficulty achieving carbon reduction goals. Currently, J-Credit is traded through negotiated transactions or official auctions. To improve price transparency, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) is planning to set up a carbon credit market based on the J-Credit scheme.
The J-Credit scheme was established to integrate Japan's domestic credit scheme and offset credit (J-VER; Japan’s verified emissions reduction) scheme and is managed by the central government with the main purpose of promoting corporate social responsibility activities and voluntary carbon offsets.
Outline of the J-Credit scheme
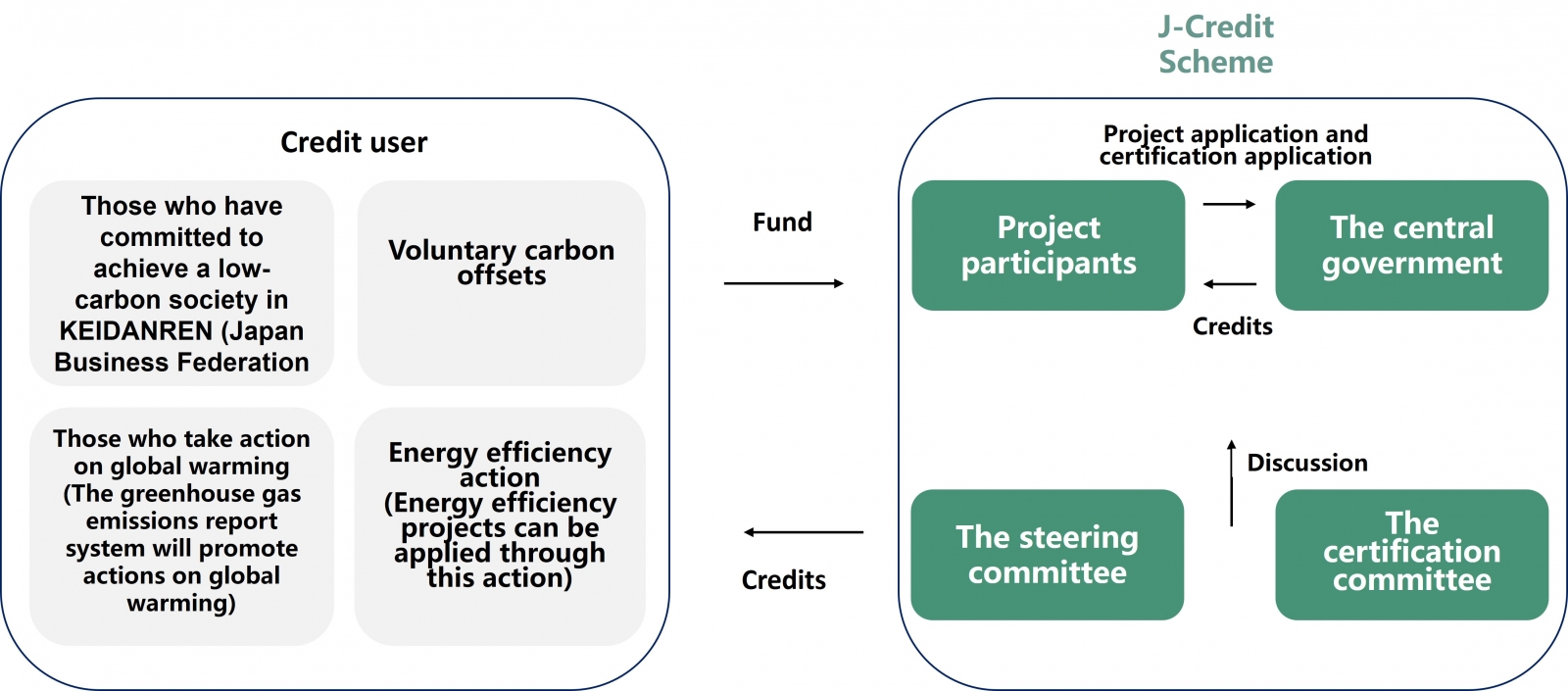
Figure I / Source:J-Credit
Registration requirements:
-
It shall be implemented in Japan.
-
It shall be implemented before, on, or within two years after the registration date of the application.
-
It cannot be the same program as projects that the certification has expired (the certification of projects ends after eight years from the start date and no later than March 31, 2031).
-
It shall be different from the projects registered in similar programs.
-
Additionality (over three years of the payment for projects/facilities) shall be met.
-
It shall be implemented according to an approved method.
-
It shall be verified by an examining agency.
-
Actions are required to maintain permanence (forest carbon sinks only).
Application procedure
PDD: Project Design Document
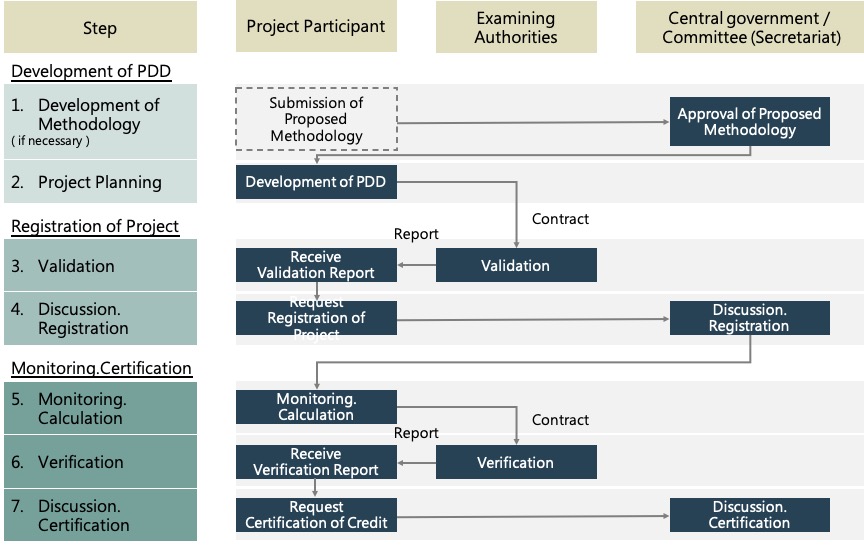
Figure II / Source:J-Credit
The inspection agency must be certified by ISO 14065 to ensure credibility. As of June 2020, there are seven qualified examining agencies:
-
Deloitte Tohmatsu Sustainability Co., Ltd.
-
Perry Johnson Registrar Clean Development
-
Mechanism, Inc.
-
Japan Management Association GHG
-
Certification Center
-
Japan Quality Assurance Organization
-
Nippon Kaiji Kyokai
Credit trade
J-Credits can be sold and purchased through bilateral negotiations or official auctions. For those who need to perform transactions, the J-Credits website will provide a list of credits sold through bilateral negotiations and official auction information.
The average prices of official auctions are as follows:
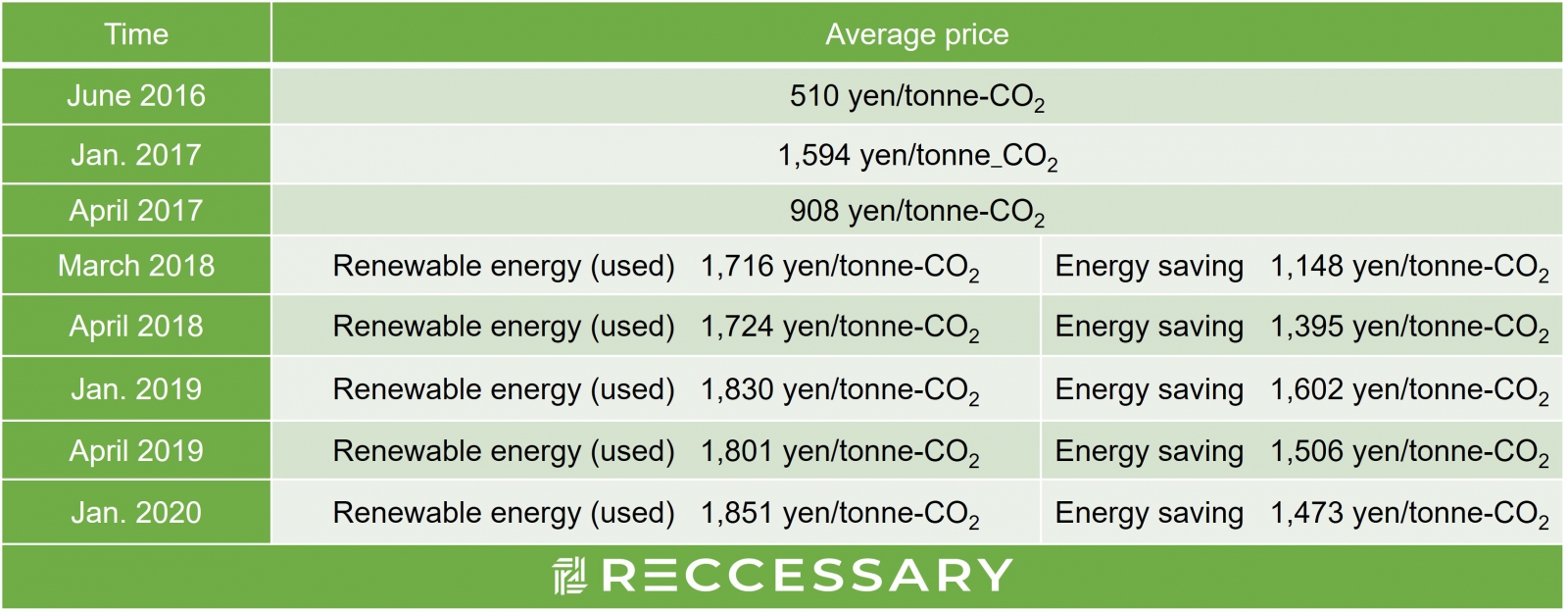
Table I / Source:J-Credit
1 The average prices are calculated by dividing the total amount (JPY) in the contract by the total trading volume (t-CO2) per auction.